
Overview
The National Museum of Australia Act is the legislation that established and governs the National Museum of Australia (NMA), a major national cultural institution located in Canberra, ACT. The museum plays a key role in preserving and interpreting Australia’s history and cultural heritage.
Sights
Map
Info
Key Points about the National Museum of Australia Act 1980:
- Establishment of the Museum: The National Museum of Australia Act 1980 was passed by the Australian Parliament to create the National Museum of Australia. The Act provided the legal foundation for the establishment and operation of the museum, with the primary goal of developing a comprehensive collection of objects, artifacts, and exhibits that represent Australia’s history, culture, and identity.
- Purpose of the Museum: The primary purpose of the National Museum, as outlined in the Act, is to collect, preserve, and display objects and artifacts that reflect the diverse stories of the Australian people. This includes the indigenous heritage of Australia, the impact of European settlement, and the development of Australian society and culture over time.
- Mandate and Functions: The National Museum of Australia Act defines several key functions for the museum:
- Collection: To develop and maintain a collection of objects that illustrate Australian history and culture, with an emphasis on inclusivity and diversity.
- Exhibitions and Research: To develop and present exhibitions that tell the stories of Australia’s people, cultures, and heritage. The museum is also involved in research related to its collections.
- Education and Public Engagement: The Act also directs the museum to provide educational resources and programs, as well as engage with the public through exhibitions, publications, and outreach.
- National Role: The museum is expected to act as a national institution that serves as a reference point for understanding Australia’s history, serving as an educational, cultural, and historical resource for the nation.
- Governance: The National Museum of Australia is governed by a Council. The Act establishes the Council to oversee the operations of the museum, ensuring its strategic direction, development, and the appropriate management of its collections. The Council members are appointed by the Australian Government, and the museum is required to report to Parliament annually on its activities.
- Indigenous Collections and Perspectives: The National Museum is committed to presenting and preserving Indigenous cultural heritage. The Act specifically highlights the importance of recognizing and interpreting the diverse cultures, histories, and experiences of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. This includes the development of exhibits that reflect the experiences of Indigenous communities, their stories, and their contributions to the development of Australia.
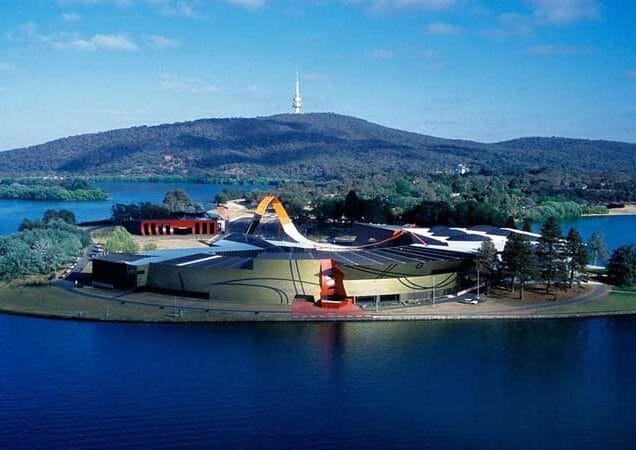
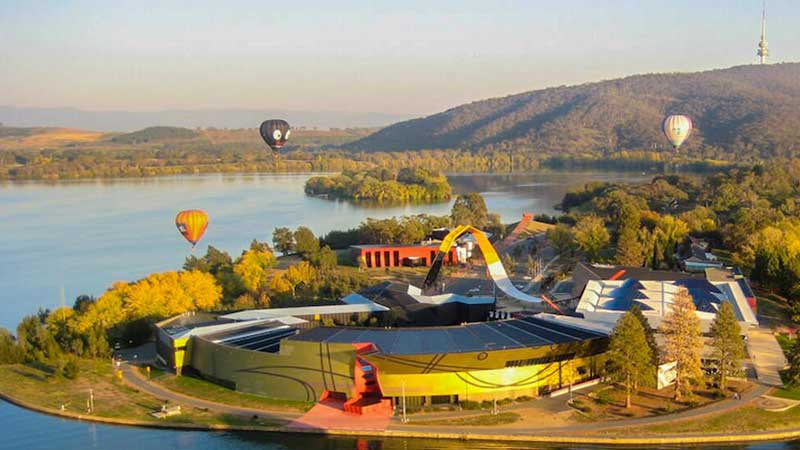
- Location and Opening: The National Museum of Australia was officially opened in 2001 and is located on the shores of Lake Burley Griffin in Canberra. The building itself is a striking modern architectural landmark, designed by the architectural firm architectus, incorporating symbolic elements reflecting Australia’s diverse history.
- The Museum’s Role in National Life: The National Museum plays a prominent role in preserving and sharing the stories of the Australian nation. It serves as a place where citizens and visitors alike can reflect on Australia’s past, understand its present, and contribute to shaping its future.
- Amendments and Updates: The National Museum of Australia Act has been amended over time to reflect the evolving role of the museum, changes in governance, and updates to its responsibilities. This includes provisions related to the protection of the museum’s collections, its financial oversight, and the continued development of its educational and public programs.
Key Functions of the National Museum of Australia as Defined by the Act:
- Exhibit and Educate: Develop, present, and curate exhibits that engage the public with the diverse and rich history of Australia.
- Preserve Cultural Heritage: Care for and maintain a collection of objects, art, and artifacts that document the story of Australia and its people.
- Research: Conduct research to expand knowledge about Australia’s history and heritage.
- Public Engagement: Engage with Australian and international audiences through exhibitions, events, and educational programs.
Notable Features of the Museum:
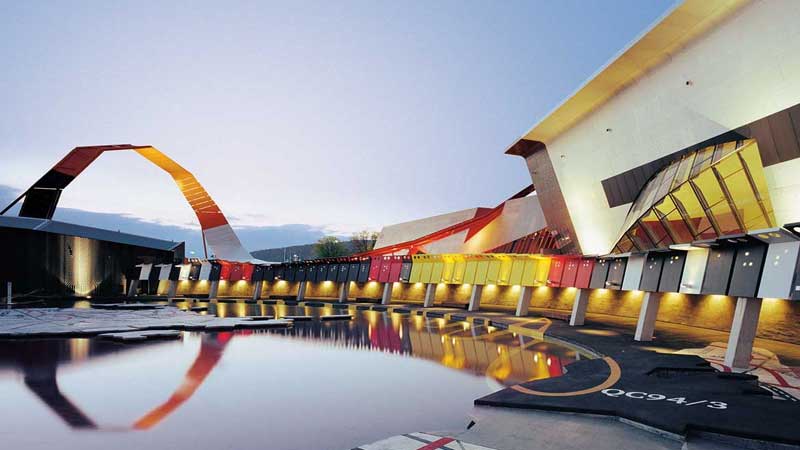
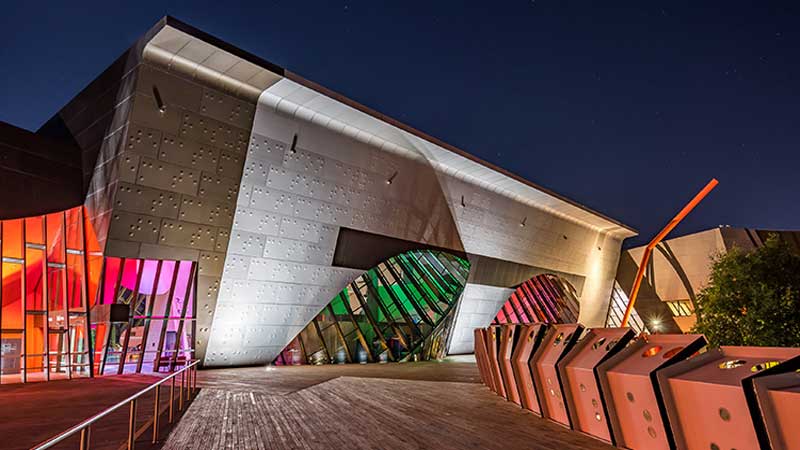
- The Building: The National Museum is housed in a striking, modern building that symbolizes the nation’s history. Its design incorporates elements that connect the museum to Australia’s cultural, social, and natural history.
- Collection: The museum’s collection includes over 200,000 objects representing the country’s diverse history, from Indigenous artifacts to modern-day objects. Highlights include objects related to early European settlement, Indigenous history, Australian democracy, and national achievements.
- Exhibitions and Programs: The museum hosts a wide range of exhibitions and special events, including traveling exhibitions, educational programs for schools, and public lectures on various aspects of Australian history.
The National Museum of Australia Today:
The museum remains an important institution in Australia, providing the public with opportunities to learn about the nation’s diverse and sometimes challenging history. It plays an essential role in fostering understanding, tolerance, and national identity by sharing the stories of all Australians, including Indigenous peoples, immigrants, and other communities that have shaped the nation.
Conclusion:
The National Museum of Australia Act 1980 established the museum as a central institution for preserving and sharing Australia’s history and culture. It provides the legislative framework for the museum’s operations and defines its role as a vital national resource for education, reflection, and the public understanding of the Australian experience. Through its collections, exhibitions, and programs, the National Museum continues to fulfill this mandate, offering a window into the diverse stories that make up Australia’s national identity.






